
In order for the global ecosystem to be in balance and work perfectly, both plants and animals are equally important and essential. Plants need animals and vice versa, but how do plants and animals relate?
Plants need animals for pollination and fertilizer, and animals need plants for food, shelter, and oxygen. Besides plants and animals needing each other for propagation and survival, they also have similarities on a cellular level, in their DNA, energy consumptions, and senses.
In this article, you will find out what relationships animals and plants have and how plants actually are a lot like animals.
Contents
Animal-Plant Relationships
Plants and animals evolve together. They are dependent on one another. Some relationships are beneficial to both parties. However, some have had a clear benefit for the expense of the other one.
There are 5 relationships between plants and animals:
Plant-Herbivore Relationship
Herbivory is an interaction in which a plant or a portion of the plant is consumed by an animal. This interaction involves bacteria and fungi that can cause diseases as they feed on plant tissue. Examples of herbivores are browsers, grazers, aphids, caterpillars, deer, and bison. Even insects that feed on seeds are considered herbivores. Some of them eat the entirety of plants, while some only eat a portion during consumption.
Herbivores and their food plants:
- Bison, sheep, grazers - succulent forbs, grasses, grass-like plants
- Deer and browsers - leaves, twigs of woody plants like willows, arborvitaes, and yews
- Beever - tree bark, young shoots, leaves
- Rodents - succulent forbs, grasses, grass-like plants
- Rabbits - succulent forbs, grasses, bark
- Voles - roots, bark
- Caterpillars - leaves
- Monarch butterfly - milkweeds
- Gypsy moth - oaks and other hardwoods
- Aphids - plant juices
- Many birds - seeds and fruits
- Locusts - all plants (seeds, leaves, and stems)
- Oilbirds - The fruit of palms and laurels
- Koala - leaves of the eucalyptus tree
- Pandas - bamboo (actually called a folivore)
- Termites - wood (actually called xylophages)
- Many insects - all plants (seeds, leaves, and stems)
- Larvae or young wormlike forms - plants' roots
Many relationships between plants and animals are mutually beneficial (symbiotic). For instance, flowers need hummingbirds to pollinate them, just as hummingbirds need the flowers' nectar to refuel. More about pollination below.

Plants-Pollinators Relationship
Pollination is the transfer of the pollen from one flower to the stigma of another, which results in fertilization. The fertile product of this process is the formation of new seeds.
Many plants depend on animals for pollination. Insects, birds, and even bats are essential for perpetuating plants. Animal pollination has advantages for plants. They cover great distances, which ensure genetic diversity through the transfer of pollen to unrelated individuals. This relationship is an example of mutualism.
Plants and animals are not just alike in their genetic components and characteristics. They are also into a relationship, where both of them can either benefit or live at the expense of the other. Nonetheless, their relation to each other is bound not just with their attributes, but also with their needs.
Plants-Animals & Oxygen Relationship
Just like humans, animals need plants for oxygen. Without plants, there wouldn't be enough oxygen on earth and animals would die.
The current oxygen cycle is driven by photosynthesis in plants, bacteria, and algae, on land, and in the lakes and oceans. Actually, the most amount of oxygen we get is from tiny ocean plants called phytoplankton. Like all plants, they photosynthesize (they use sunlight and carbon dioxide to make food for themselves and a byproduct of this process is oxygen).
Scientists believe that only phytoplankton contributes between 50-85 percent of the oxygen in the earth's atmosphere. Below is a picture (by earthobservatory.com) of phytoplankton in the ocean.

If you like this article, check out Why are Fungi not Plants?
Plants-Animals & Shelter Relationship
Some animals need plants for shelter - like many birds make nests from dead branches and or other organic stuff. Besides birds making nests a lot of other animals use trees to live, sleep, hide, eat, and/or hunt. Not only trees are used for these practices, but other plants like bushes or dead trees as well.
The next group of animals like sloths, koalas, flying snakes, geckos, tarsiers, and opossums who all live in trees for the majority of their lives are called arboreal animals.
Arboreal animals are evolved to live their best life in tree-tops. They all have special features like claws, long arms, or wings to easily climb trees and live in them.
Plants-Animals & Compost Relationship
Animals provide some of the compost (nutrients) for plants. They do this in two different ways:
- With animal feces.
- Nutrients from dead animals are absorbed by plants.
When an animal goes to its outdoor-bathroom next to a tree. The feces of the animal will dissolve in the soil and eventually, the tree will absorb the nutrients that were in the feces. Just like a farmer uses fertilizer.
Also when an animal dies, it decays and the nutrients from its body go back into the earth where they are absorbed by plants.
The similarities between plants and animals
Plants and animals are both living things. At first, it might seem that they are not similar to one another. Plants can not walk and eat, while animals can catch their prey and look for potential food, including plants. However, scientists have argued that these two living things have more characteristics in common than differences.
Both plants and animals are part of the living things on Earth. It means that both classifications have DNA, made up of cells, and require energy to live.
Cellular structure
Cells are the smallest functional units of all living organisms. Plants have cell walls while animals do not. Their cells contain different organelles that are tiny structures, performing different functions. However, plants and animals cells can serve the same basic functions, like absorbing nutrients to convert them into energy.
Like you can see in the picture below, animal cells and plant cells are almost identical. The only difference is that a plant cell has Chloroplast, a permanent vacuole, and a cellulose cell wall.
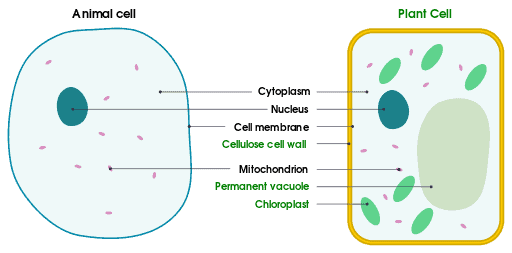
Image by: Domdomegg
DNA
DNA is referred to as the blueprints of life. It is a long chain of amino acids that can form together to create a specific living thing. With this, both plants and animals have DNA in their cells. Through the sequencing of DNA cells, scientists have found out how similar and related living things are to one another.
In humans, a DNA test is used to prove one's relation with one claimed relatives. It is also the case for plants and animals. Through a genetic test, their connection to each other can be proven despite its extremely distant.
Energy consumption
Eating food is essential to living things. But, it may vary on how they get their nutrients. Nonetheless, food is needed to support one's body and to keep all its systems working. Cells convert the nutrients in our food and make it into reusable energy that can support us with daily activities.
Humans and animals may consume food from the things that surround them, especially from natural resources. And just like them, plants also ingest what is around them to support their system. They can be different since they are not able to eat, they can only absorb. However, they need the energy to grow and function properly in our environment.
Plants can get their nutrients by absorbing them via their roots, or by simply receiving energy from sunlight through photosynthesis (see picture below). Through the plastids in plant cells, nutrients from sunlight are broken down and converted into energy, just like carnivores do.
Picture by: Charlotte Roy and Salsero35
Senses
You must be wondering why senses are included in their similarities. It will require the eyes, nose, tongue, skin, or ears to technically say that a living organism has senses. However, it is not the same for plants.
All living things can sense the world that surrounds them but may differ in ways. For animals, both vertebrates and invertebrates usually have most of the five senses that humans have. They can feel through their skin, hear through their ears, see through their eyes, and some of them can even speak through their mouth with animal language.
However, in the case of plants, they do not have any sensory organs. Instead, they use their hormones and sensory ions and process information that are around them. They can feel light that is why they can absorb it as their main energy. Plants can also sense whether the sun is still out or down.
Think about it, for example, a houseplant that grows towards the window because the light comes from there, or maybe closing the pores on their leaves during night time.

Picture by: Tangopaso
In a study published at PLOS ONE, researchers have discovered that plants can have an actual interaction with one another, despite the absence of sensory organs.
Plants and animals may seem like two different entities due to their physical appearance. However, they are undoubtedly related to one another, whether you believe it or not. They are both living things, and that means they have a lot of common characteristics, which may vary in the way it is shown to them. They both require the same thing to remain healthy.
With their similarities and differences, these two also have the potential to benefit from each other. Plants could be the food source for animals, while animal wastes can be a fertilizer to help plants grow healthier. Nonetheless, they are still connected. Regardless if they are minding their own business, or they are using each other to survive.
If you are still not convinced, then you need to read more books about biology! Or just simply read my other articles!



Leave a Reply