
Nitrogen is considered to be the most important nutrients for plants that helps maintain good health and regulate the proper amount of growth. But how do plants get their nitrogen?
Plants get their nitrogen by a natural nitrogen cycle, in which the nitrogen in the air will be converted into an absorbable form of nitrogen for plants. Plants can also get their nitrogen through fertilization of the soil.
In this article, you will learn everything about nitrogen in plants, why it's there, and how plants get their nitrogen. Let's start!
Contents
- How Do Plants Get Nitrogen?
- 5 Phases Of Nitrogen Cycle Explained
- Phase 1: Nitrogen Fixation
- Phase 2: Mineralization
- Phase 3: Nitrification
- Phase 4: Immobilization
- Phase 5: Denitrification
- Nitrogen From Fertilizers
- 6 Reasons why plants need nitrogen to live
- How to find out if there is enough nitrogen in the soil?
- How to fix nitrogen deficiency in soil?
- Too much nitrogen in the soil? Do this...
How Do Plants Get Nitrogen?
The presence of all the required chemical compounds in a fixed and required amount will lead to the healthy development of a plant. Among all the important chemical compounds required by the plant, nitrogen is one of them and there are actually only two ways how plants get nitrogen:
- From the natural nitrogen cycle.
- From fertilizers.
In order for the plant to naturally take in nitrogen from the ground, there is something called the nitrogen cycle which helps transfer nitrogen from the air to an absorbable form of nitrogen. More of that in a minute...
Although Nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements in the earth but still in the plants the common deficiency problem is related to nitrogen, this is because nitrogen from the atmosphere or from the earth's crust is not directly available for the plants. This deficiency can be fixed by adding fertilizer to the soil. The fertilizer can be absorbed by the plant and used as nitrogen.
5 Phases Of Nitrogen Cycle Explained
While nitrogen is a very important chemical for plants, plants do not simply absorb the nitrogen out of the air. To absorb nitrogen, there are 5 phases of the nitrogen cycle. What is the nitrogen cycle you might ask? I did some research and found the following:
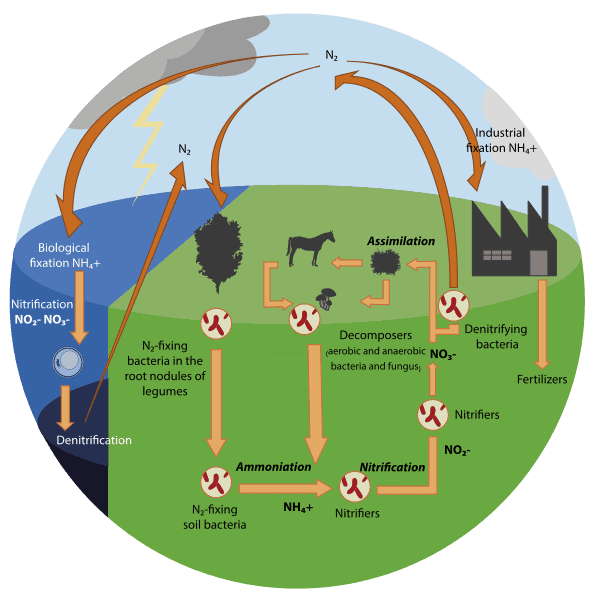
Image by: WikiCommons
Phase 1: Nitrogen Fixation
In the first phase of the nitrogen cycle, the nitrogen moves from the air into the ground. Because plants can't just use the nitrogen (N2) from the air, the nitrogen from the air must be transformed through a process called nitrogen fixation into an absorbable form - for example: NO2, NO, NH3 or NH4NO3.
Most of the nitrogen fixation occurs naturally in the soil by bacteria (see picture above. Some bacteria attach to plant roots and have a symbiotic (beneficial for both) relationship with the plant. The bacteria get energy through photosynthesis and in return, the bacteria fix nitrogen in the form that the plant needs.
A small amount of nitrogen can be fixed by lightning. When the lightning provides enough energy for the nitrogen in the air to react with oxygen and nitrogen oxide (NO) will be formed which will then find its way to the soil through rain or snow.
Phase 2: Mineralization
This phase takes place in the soil of the plants. Nitrogen moves from organic matirials, such as plant to an inorganic form of nitrogen that plants can use. Decomposed plants are being used for nitrogen in other plants as well as animal materials that are left on the soil.
Mineralization starts when microbes decompose organic material and begin converting it to a form of nitrogen that can be used by plants. The first form of nitrogen produced by this process is ammonia, NH3. This ammonia will react with water to form ammonium NH4, which will be available for plants.

All plants, except legumes, get the nitrogen they require through the soil. Legumes fix their own nitrogen through their root system.
Phase 3: Nitrification
The next phase called nitrification also takes place in the soil. During nitrification, the ammonia in the soils, produced by mineralization, is converted into compounds called nitrites, NO2-, and nitrates, NO3-.
Nitrates can be used by plants and animals that consume the plants.
However nitrites are not usable by plants and animals directly, some bacteria can change nitrites into nitrates, with the help of oxygen, and in the process getting energy out of it. The nitrates then can be used as nitrogen for the plants.
The process of nitrification is important for plants and will make sure the plants always have enough nitrogen available if they need some.
Phase 4: Immobilization
Microorganisms in the soil use the same forms of nitrogen that plants use in order to survive. When the bacteria in the ground would use up all the nitrogen, the plants would soon be deficient in nitrogen.
That is why immobilization ties up nitrogen in microorganisms and helps to maintain balance the amount of nitrogen in the soils by tying it up or immobilizing the nitrogen in microorganisms.
Phase 5: Denitrification
In the fifth and last phase of the nitrogen cycle, the nitrogen that is used in the soil is converted back to atmospheric nitrogen (N2) by bacteria - this process is called denitrification.
if you like this type of content, check out: Why is it Bad to Put Rocks at The Bottom of a Plant Pot?
Nitrogen From Fertilizers
When there is a deficiency of the nitrogen in the soil, the plant lacks the proper growth and development and tends to die faster. This is why to fulfill the need of the nitrogen in the plant which is not being fulfilled by the soil, we generally use the fertilizers rich in nitrogen components.

The mostly used nitrogen fertilizers are ammonium nitrate, calcium ammonium nitrate, urea, fertilizer with nitrogen and sulfur, etc. There are several fertilizers that are present in the market which helps in the fulfillment of the nitrogen in the plants.
Thus, plants get their nitrogen both naturally as well as synthetically. Both ways are reliable. If the plant gets the nitrogen naturally then it is the best available option, majorly from the soil but if the soil does not contain enough amount of required nitrogen then the fertilizers must be used to fulfill the requirements.
6 Reasons why plants need nitrogen to live
Nitrogen is an essential component of chlorophyll
This is the compound by which plants use sunlight energy to produce sugars from water and carbon dioxide.
Nitrogen helps in building the protein blocks in the plant
This chemical is abundant in the amino acids of the plant and you must be aware of the fact that the plants need the proteins to be healthy as well as to survive. These proteins are really essential for the plant as they act as a structural unit in the plant cells while others act as enzymes which makes many of the biochemical processes possible in the plants to sustain life in it.
Nitrogen also is very useful for the reproduction process of the plant.
Nitrogen works as an energy transferring component
This compound helps transfer energy in the adenosine triphosphate. This ATP allows the cells to conserve and use the energy released in metabolism.
Nitrogen is also a vital component present in the nucleic acids
It is for example present in DNA that allows the growth and reproduction in the cells. So, without nitrogen life is not quite possible in plants as far as we know.
Nitrogen is essential to achieve maximum harvest potential
One of the most critical components of the amino acid in protein and thus it also increases the protein content of the plant.
How to find out if there is enough nitrogen in the soil?

In order to find out if the soil is nitrogen deficient, you can test the soil. one way to test the soil is to ask your local farmer, maybe he can test the soil for you.
Another way to test if there is enough nitrogen in the soil is to buy a test kit.
You can buy your own soil testkit online...
How to fix nitrogen deficiency in soil?
When there is a nitrogen deficiency in the soil, you have two options to fix the nitrogen in the ground.
Natural nitrogen deficiency sollution:
- Adding composted manure to the soil.
- Planting a green manure crop such as borage.
- Planting nitrogen-fixing plants like legumes like peas or beans.
Chemical nitrogen deficiency sollution:
- Chemical fertilizers.
Too much nitrogen in the soil? Do this...
There are actually two things you can do to reduce the nitrogen in the soil. Here are the two things:
- Using plants that will reduce nitrogen in the soil (squash, cabbage, broccoli, and corn).
- Use mulch to remove excess nitrogen in the soil (as the mulch breaks down, it depletes the nitrogen in the soil).



Leave a Reply